How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that blends technical understanding with responsible practice. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering controls, capturing stunning aerial footage, and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Whether you’re a novice eager to learn or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, ensuring you can confidently and safely enjoy the world of drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various drone components and adhering to safety regulations. Failure to do so can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone’s airworthiness. The following checklist should be completed before every flight.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires a good grasp of the fundamentals, and a helpful resource for learning this is available at how to operate a drone. This site offers valuable guidance on safe and effective drone piloting, ensuring you’re well-prepared before your next flight.
| Component | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or wear. Securely attached? | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s properly seated. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. | |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Clean the lens if necessary. | |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. | Sufficient satellites are needed for accurate positioning. | |
| Gimbal | Check gimbal movement and stability. | Ensure smooth and unobstructed movement. | |
| Radio Connection | Test the connection between the drone and remote controller. | Check for signal strength and interference. | |
| Flight Controller | Verify proper functioning of the flight controller. | Observe for any unusual behavior during pre-flight checks. |
Essential Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Adhering to safety regulations is paramount for responsible drone operation. These guidelines help prevent accidents and ensure compliance with the law.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Operate your drone within the legal weight and distance limits.
- Be aware of surrounding obstacles and avoid collisions.
- Never fly your drone in adverse weather conditions (high winds, rain, etc.).
- Familiarize yourself with local regulations and obtain necessary permits.
- Fly responsibly and avoid disturbing wildlife or other people.
Safe Flight Conditions Decision-Making Process
A flowchart helps determine if flight conditions are safe before initiating a flight. It’s a visual representation of the decision-making process.
[Flowchart would be inserted here. A simple textual description follows:] Start -> Check weather (wind speed, precipitation)
-Yes (safe) -> Check airspace restrictions – Yes (safe) -> Check battery level – Yes (safe) -> Proceed to flight. No (unsafe) at any point -> Postpone flight.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Swift and appropriate action can minimize damage and prevent accidents.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually guide the drone back using visual cues.
- Malfunction: Attempt to land the drone in a safe, open area. If unable to control the drone, prioritize safety and avoid populated areas.
- Battery Failure: Initiate RTH immediately. If RTH is unavailable, attempt a controlled emergency landing.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone controls is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers the basics of drone control and navigation techniques.
Drone Remote Control Functions
A typical drone remote controller features several control sticks and buttons, each serving a specific function. Understanding these controls is key to precise maneuvering.
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical/Horizontal) | Controls the drone’s altitude and forward/backward movement. Pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases altitude. Pushing it forward moves the drone forward, pushing it back moves it backward. |
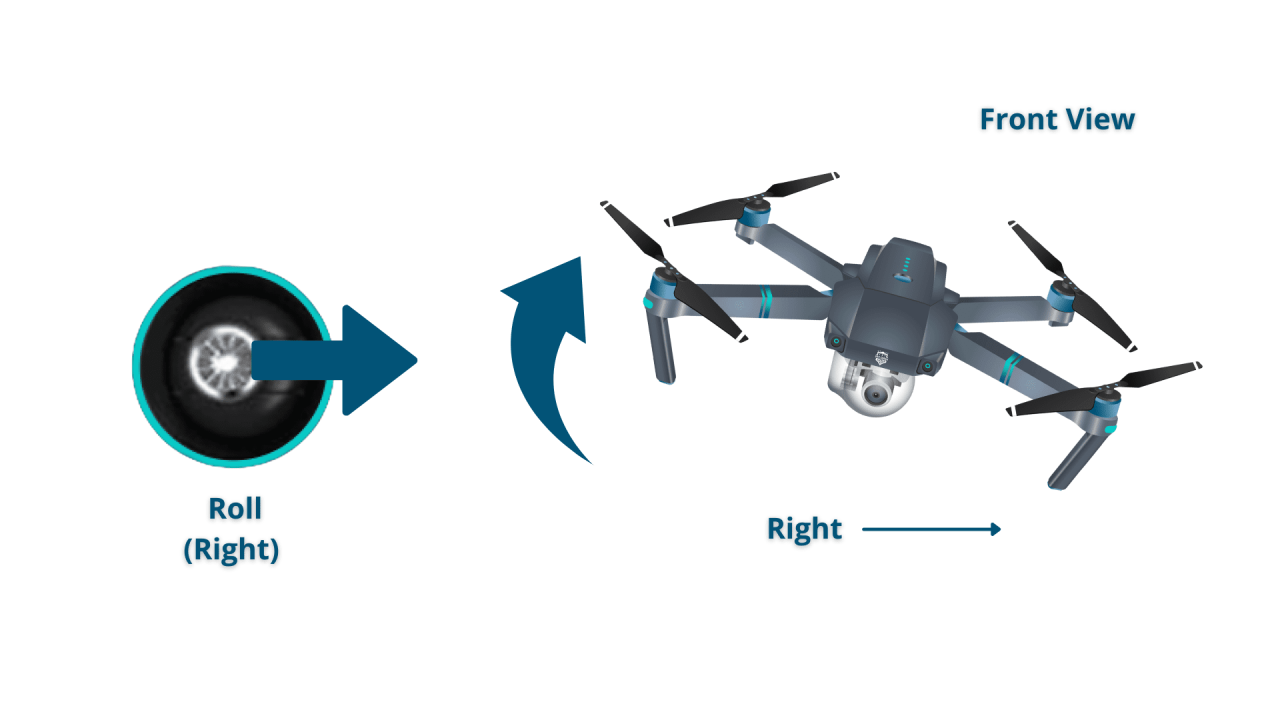
| Right Stick (Yaw/Lateral) | Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and left/right movement. Pushing the stick left rotates the drone counter-clockwise, pushing it right rotates it clockwise. Pushing it left or right moves the drone laterally. |
| Return to Home (RTH) Button | Initiates the automated return-to-home function, guiding the drone back to its starting point. |
| Camera Control Buttons | Used to adjust camera settings, such as zoom, photo/video recording, and gimbal orientation. |
| Power Button | Turns the drone and remote controller on and off. |
Smooth and Precise Drone Maneuvering
Smooth and precise maneuvering requires practice and understanding of the drone’s responsiveness. Mastering hovering and precise movements enhances the quality of aerial footage.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position by making small, controlled adjustments with the control sticks.
- Precise Movements: Use small, incremental movements of the control sticks to achieve precise positioning and avoid jerky movements.
- Practice: Regular practice in a safe, open area helps develop smooth and controlled flight techniques.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability, catering to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Choosing the appropriate mode is essential for safe and efficient operation.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, providing greater stability for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Increases the drone’s speed and responsiveness, allowing for more dynamic maneuvers. Requires more skill and practice.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for position holding and RTH functionality.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of its position. Useful for precise movements.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration is crucial for precise navigation and stable flight. Regular calibration ensures reliable positioning and prevents drift.
- Compass Calibration: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the drone’s compass in an open area, away from magnetic interference.
- GPS Calibration: Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before flight, allowing the drone to accurately determine its position.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and employing effective composition techniques. This section details how to achieve optimal image quality.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Proper adjustment of camera settings is crucial for optimal image quality in diverse lighting conditions. Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is essential for achieving desired results.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-number) allows more light, resulting in a shallower depth of field (blurred background). A narrower aperture (higher f-number) allows less light, resulting in a deeper depth of field (sharper background).
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. A faster shutter speed freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed can create motion blur.
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. A lower ISO produces less noise (grain) but requires more light. A higher ISO produces more noise but allows shooting in low-light conditions.
Camera Angles and Compositions
Different camera angles and compositions can dramatically impact the visual appeal of aerial shots. Strategic use of angles enhances storytelling and visual interest.
- High Angle: Provides a broad overview of the scene, showcasing the overall landscape or environment.
- Low Angle: Emphasizes the subject’s size and grandeur, creating a dramatic perspective.
- Bird’s Eye View: Captures a directly overhead perspective, ideal for showcasing patterns and textures.
- Dutch Angle: Tilts the camera to create a sense of unease or dynamism.
- Following Shot: The camera follows a moving subject, maintaining a consistent distance.
Intelligent Flight Modes
Intelligent flight modes simplify the creation of creative aerial shots, providing automated movements and camera control. These modes add versatility and enhance storytelling capabilities.
- Point of Interest (POI): The drone orbits a designated point, allowing for dynamic shots.
- Orbit: Similar to POI, but allows for customizable orbit radius and speed.
- Waypoint: The drone follows a pre-programmed path, capturing shots at specific locations.
- Follow Me: The drone automatically follows a designated subject, keeping it centered in the frame.
Best Practices for High-Resolution Photos and Videos
Following best practices ensures high-resolution image quality. This checklist summarizes key aspects for capturing optimal aerial footage.
- Use a high-quality SD card.
- Shoot in the highest resolution setting possible.
- Avoid shooting in extremely bright or dark conditions.
- Maintain a steady flight for sharp images and videos.
- Regularly check and clean the camera lens.
- Properly adjust camera settings for the specific lighting conditions.
Drone Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery management and regular maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring safe operation. This section Artikels essential practices.
Battery Charging and Storage

Correct charging and storage techniques significantly impact battery longevity. Following these guidelines helps maximize battery performance and lifespan.
- Use only the manufacturer-recommended charger.
- Avoid fully discharging the battery.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
- Do not leave batteries charging unattended.
Signs of a Failing Drone Battery
Recognizing the signs of a failing battery is important for preventing unexpected failures during flight. Early detection allows for timely replacement.
- Reduced flight time.
- Swollen battery.
- Unusual heating during charging or operation.
- Inconsistent performance.
- Low voltage warnings.
Routine Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures the drone remains in optimal condition. This prevents potential issues and prolongs its operational lifespan.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean propellers and body | After each flight |
| Inspect for damage | Before each flight |
| Calibrate sensors | As needed |
| Check battery health | Before each flight |
| Firmware update | Periodically (check manufacturer recommendations) |
Troubleshooting Battery Issues, How to operate a drone
Troubleshooting common battery issues helps maintain optimal drone performance. This section Artikels steps to address common problems.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- Sudden Power Loss: Inspect the battery connections and check for damage.
- Reduced Flight Time: Check battery health and consider replacing if necessary.
- Swollen Battery: Immediately remove and dispose of the battery safely.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines. This section Artikels crucial considerations for safe and legal drone operation.
Regulations and Legal Requirements

Different locations have varying regulations regarding drone operation. Understanding these regulations is crucial to avoid legal penalties.
| Location | Regulations | Penalties |
|---|---|---|
| [Example Location 1] | [Specific regulations for this location, e.g., registration requirements, airspace restrictions] | [Penalties for violations, e.g., fines, license suspension] |
| [Example Location 2] | [Specific regulations for this location] | [Penalties for violations] |
Note: This table provides examples only. Always consult the specific regulations for your location.
Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation goes beyond legal compliance; it also involves ethical considerations that ensure the safety and well-being of others.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before attempting complex maneuvers; a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to emergency procedures. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation.
- Respecting privacy: Avoid flying over private property or recording individuals without their consent.
- Avoiding dangerous flight maneuvers: Do not fly recklessly or endanger others.
- Environmental awareness: Be mindful of wildlife and the environment.
Commercial Drone Operation
Operating a drone commercially involves additional legal requirements and responsibilities. Obtaining necessary permits and licenses is essential for legal and ethical operation.
- Research local and national regulations for commercial drone operations.
- Apply for the appropriate licenses and permits.
- Maintain insurance and liability coverage.
Responsible Drone Operation Guide
Responsible drone operation prioritizes safety, respect, and legal compliance. This guide summarizes key aspects for ethical and safe drone usage.
- Always check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly near airports or restricted airspace.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Follow all applicable laws and regulations.
- Be aware of your surroundings and avoid collisions.
- Fly responsibly and ethically.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and responsible practice. By understanding the technical aspects, adhering to safety regulations, and embracing ethical considerations, you can unlock the full potential of aerial technology while ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience for yourself and others. Remember to always prioritize safety and respect the airspace around you. Happy flying!
Query Resolution
What is the maximum flight time for a typical drone battery?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery size. Check your drone’s specifications for accurate information; generally, expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes per battery charge.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures. In many places, registration is mandatory for drones exceeding a certain weight.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency procedures Artikeld in your drone’s manual. If unsuccessful, attempt to land it in a safe, open area away from people and property. Contact local authorities if necessary.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass and GPS?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass and GPS before each flight, especially if you’re flying in an area with magnetic interference or after a crash or hard landing. Your drone’s manual will provide specific instructions.
